Five Insights When Developing Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)


Developing Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is more than a technical challenge, it is a regulated process where clinical safety, software quality, and robust documentation intersect. As the medical device industry increasingly integrates digital capabilities, understanding and applying the right development practices become critical. IEC 62304, the international standard for medical device software, provides the framework, but applying it effectively requires a hands-on mindset. Here are five key insights that every development team should consider.
1. Ensure End-to-End Traceability from Requirements to Tests
Traceability is not just a documentation requirement, it is central to demonstrating control, safety, and intent throughout the software lifecycle. Each requirement must be clearly linked to its corresponding design, implementation, and test cases. Maintaining this chain helps manage changes safely and supports audit-readiness. Making traceability part of daily development routines, through consistent naming, reference IDs, and trace logs, ensures your system evolves without losing oversight.
2. Structure Your Architecture Around Risk Classification
Not all software components carry the same level of risk. IEC 62304 mandates that safety-related software be classified as Class A, B, or C, based on potential harm to users or patients. Designing your system architecture to isolate higher-risk modules allows targeted testing and documentation where it matters most. This approach helps teams manage regulatory burden without compromising agility and supports effective traceability and impact analysis later.

3. Continuous Verification Through Code Reviews Ensures a High Development Standard
In a SaMD environment, software quality directly impacts patient safety. Implementing structured and continuous code reviews ensure that every change is validated by multiple eyes, catching defects early and aligning with IEC 62304’s verification requirements. Beyond functionality, reviewers should evaluate maintainability, potential risk implications, and adherence to safety classification constraints. Code review becomes a tool not just for quality, but also for accountability and traceability.
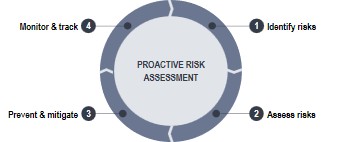
4. Integrate Risk Management into the Development Process
IEC 62304 requires that software development be fully integrated with risk management per ISO 14971. This is mot a one-off FMEA, it is a continuous activity. Developers should understand how their work affects safety-related functions, and how software failures can contribute to hazardous situations. Encourage a culture where risk ownership is shared across engineering, not siloed in quality or regulatory functions.
5. Make Documentation a Natural, Ongoing Part of Development
Rather than being an afterthought, documentation should evolve hand-in-hand with your code and design. Capturing rationale, decisions, and test outcomes as part of your normal work routines make documentation more accurate and much easier to maintain. This approach also helps ensure that knowledge doesn’t live only in individual developers’ heads and prepares your team for audits and scalability without unnecessary rework.
Developing Software as a Medical Device is a balance of agility and precision. With the right practices, rooted in IEC 62304 but adapted for modern development workflows, teams can deliver safe, effective, and auditable software without compromising speed or innovation. At Triathlon Healthtech, we support clients in navigating this balance through strategy, process design, and hands-on development leadership.